
AIM – Activity Information Modeling
.AIM – Activity Information Modeling captures the activity as the nucleus of organizational endeavor. It then surrounds it with other data attributes that are needed to analyze and solve the specific problems and goals of the client. It adds metadata, such as the complexity level of processes. Finally, it calculates time and cost for each.
The Activity Information Modeling Data Cube
AIM – Activity Information Modeling captures the activity as the nucleus of organizational endeavor. It then surrounds it with other data attributes that are needed to analyze and solve the specific problems and goals of the client. It adds metadata, such as the complexity level of processes. Finally, it calculates time and cost for each.
Activity Information Modeling Concepts & Principles
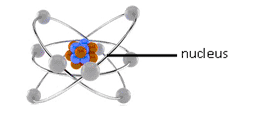
1. Activity Information Modeling is based on the principle that the activity is the primary core element of all endeavors, like the nucleus of an atom.
2. Understanding the activity, what occurs, what is achieved, why it occurs, who conducts it, its time, financial and incidence metrics, and other attributes, provides a new and powerful way to understand all facets of an organization, customers, products, processes and resource,(CP2R).
3. All activities are quantitative and homogenous, thus inherently creating a natural array of datapoints to construct a quantitative data cube with time, financial, and incidence metrics.
4. Every datapoint in the AIM data cube is related to an activity, and inherits its time, financial, and incidence metrics. This activity-based data is transformed to “information” – facts that convey knowledge. For instance, a simple product list will have time and financial metrics that identify the product with the highest cost, the lowest resource time, etc.
5. The AIM Data cube depicts a cube with 24 facets, each facet containing more than 30 segments (rows). This picture makes it easier to imagine an AIM data base cube.
6. Variable bias risk, the statistical risk of creating a data variable list that favors an outcome, is eliminated with a reverse design process that starts with the clients’ new results goals. The AIM design process is fully explained in the Private AIM section.
7. The descriptive attributes of an activity are extensive and technically infinite. AIModels can provide information about any problem and opportunity.
8. AIModels are created with a 98% confidence factor, often higher. Traditional consulting data has at best, a +/- 70% confidence factor because the sample sizes are very small and the data is qualitative because variable bias risk is common. AIModels are built with thousands of quantitative data records, each record having 20 or more data points.
9. AIM data are collected with Orient Point’s “AIM Sampler”, a random sampling application that captures work data wherever and however employees are working. Data can be collected simultaneously from an unlimited number of people, in an unlimited number of locations, on multiple continents and in multiple languages. Until delivered to clients, the data resides on Orient Point’s servers which fully comply with all local jurisdiction regulations for protected personal information.
10.Activity Information Modeling captures the activity as the nucleus of organizational endeavor. It then surrounds it with other data attributes that are used to analyze and solve the specific problems and goals of the client. It adds metadata, such as the complexity level of processes. Finally, it calculates time, cost, and incidence for each field such as resource time spent on products and the cost of each customer segment.
AIM – Activity Information Modeling captures the activity as the nucleus of organizational endeavor. It then surrounds it with other data attributes that are needed to analyze and solve the specific problems and goals of the client. It adds metadata, such as the complexity level of processes. Finally, it calculates time and cost for each.
The AIM Data Cube
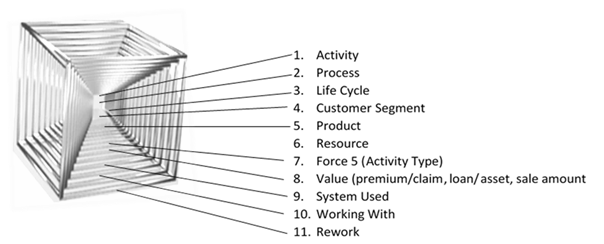
This example lists common data and meta data fields that are frequently used. Any data attribute field can be incorporated into an AIModel. We have never failed to be able to provide a client with unique information that they needed for their analyses and decision making.

CP2R (CPR) is our acronym for Customers, Products, Processes, and Resources. This is the primary scope and focus of a typical AIM project. This scope is far broader than traditional consultant’s scope.
Traditional consultants select a single area such as process and only work on that. They don’t assemble information about anything beyond the small area they’re focused on. This results in recommendations that are not feasible because of unaccounted impediments and constraints in other areas. This small scope also produces small tangible benefits.
AIM projects have also been conducted in staff functions such as Accounting, IT, HR, etc. with much success. The scope of a staff AIM project modifies our usual CPR scope.
Customer AIModels
Customer AIModels provide time and cost information about customers, customer segments, and customer activities.
The customer models are used to understand the customer segments, and often note those that have the lowest and highest ROI. It’s common for our clients to modify their target markets/customer segments, sometimes even eliminating a segment because they discover the low profits it produces.
Product AIModels
The product models are used to compare all products to find those that produce the highest and lowest margins.
The AIM product model information makes it easy to see a complete 360-degree view of the cost and resource capacity requirements for the entire product portfolio in one simple report.
Process AIModels
The process models provide information about lost productivity, poor quality and retention areas. These are generally quick, simple fixes that only require simple operation changes.
Chubb Specialty, the specialty lines division of Chubb Insurance in Simsbury, Connecticut, used their AIM process models to design a tri-track renewal process that produced a large, multi-year growth spurt, increased their productivity over 50%, and achieved record high customer retention rates.
Resource AIModels
The resource models explain how every minute of the entire organization’s resource capacity is consumed by customers, products, and processes. This information is used to improve job positions, organization design, and resource performance.
Add Your Heading Text Here

Gary Meyer invented Activity Information Modeling in 1997. Gary was a Senior Consultant with Chatham Consulting Group Inc during the 80’s where some of his clients were Citibank, American Express, Swiss Bank, Chase & AIG. Chatham was an operations consulting company worked with large financial service companies. After Chatham, Gary joined Johnson & Higgins, a global insurance broker where he created an operations management department. Marsh & McLennan merged with J&H and Gary continued as VP of Operations Management Services of Marsh until early 1997 when he left to start Orient Point Consulting LLC.
Our clients re-engage us year after year to deliver AIModels throughout their organizations because they get better, faster results, and more economically than traditional improvement/transformation methods they have used in the past. On our twentieth anniversary, we were still engaged by two of our first three clients, Citibank and Chubb Insurance, and by two other companies with executives that had worked for Citi and Chubb who then engaged us at their new companies.
AIModels are specifically designed to solve each client’s problems and achieve their goals. You’re probably familiar with data models. But data doesn’t tell you anything and it can’t be used for decision making. We build information models, not data models. AIModels provide the time and the cost of every field and variable and allow for an unlimited array of attributes.
Activity Information Models are also valuable to staff units besides Operations.
• Accounting & Finance use our cost models for their reporting and forecasting. They find the cost ratios and metrics especially useful for budgeting.
• Human Resources use our resource models to document the scope of job positions and the skills they require. Our reports show them exactly what each job actually does and how they do it.
• Marketing uses the Product AIModels to create growth program scenarios and portfolio balancing that optimize product portfolio profitability. This is always a totally new capability for them.
• IT uses AIModels to understand how systems are used and by whom. They can also spot redundancies in their technology infrastructure. Finally, they can see the processes and activities that need greater automation and technology and what the ROI would be if they build them. Our first project with Citibank in 1999 found 7 separate systems that all handled the same transactions for groups of similar credit products. Citi managers immediately consolidated the 7 to 3 systems and reduced these to one system within 18 months. This small peripheral finding, unrelated to the project’s goals, produced annual IT savings over $250,000.
• C-suite executives use AIModels to compare units’ & locations’ performance with metrics such as productivity and cost per 1K of revenue. Our succinct performance metrics helps them understand what actually drives growth and profits in their businesses.
AIM Exhibits
There are 2 AIM exhibits shown here.
Pease see the AIM Exhibits Section
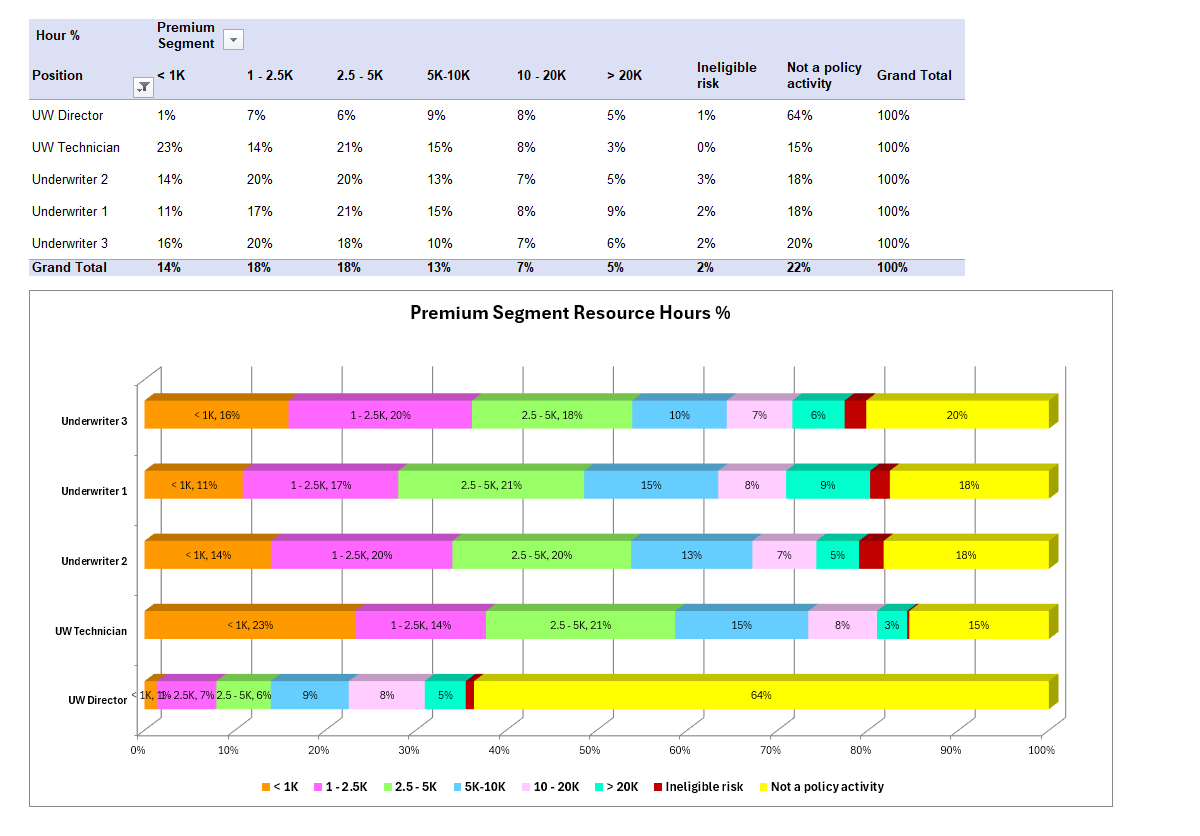
Comparing Time & Motion Studies to Activity Information Modeling


T&M requires accurate volumes to calculate total times. This is available in manufacturing where the number of processes, completed operations, and products produced is known. It is not available in most service operations where processes vary depending on the condition and needs of customers. For instance: an insurance auto claim process might have 3 steps or 33 steps, depending on a large number
of variables that can affect what a claims examiner has to do to settle it.
Activity information modeling creates information about the entire organization, customer product, process and resource information, referred to as CP2R. AIM models also proof with the General Ledger.
AIM does not require volumes to calculate time and cost.
Random Sampling & AIM Comparison
Random sampling is a statistical method for collecting data. At random times it collects data, called a sample. Random sampling is only a data collection method. Traditional consultants also collect data with surveys and interviews, observations, and by obtaining transactional data from clients production and distribution systems.
AIM employs random sampling to collect data from employees as they work. AIM has a structure that makes the data highly valuable information that is easy to use. For instance, AIM process modes have Force 5 metadata that classifies every activity into one of five types. Citibank used its AIM Force 5 models to analyze how much time its branch personnel spent on management activities, relationship
activities, knowledge activities and transactional activities.
To understand Activity Information Modeling and how it creates a new world of management information that achieve new results, please look at the AIM exhibits in Exhibits.
